| [1]张海英,盛树东,薛洁,等.三七止血与抗血栓作用的实验研究[J].新疆医科大学学报,2012,35(4):487-490.[2]Qiang H,Wang GS,Zhang C,et al. Effects of Panax notoginseng saponins on hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in cultured rabbit bone marrow stromal cells. Acad J XJTU.2010;22(1):25-29. [3]郭福.三七对骨重建偶联中细胞因子IGF-1, IL-6表达影响[J].中医临床研究,2011,3(15):20-21.[4]杨军,任婷,李学东,等.三七总皂甙促进骨折愈合作用的实验研究[J].医学研究杂志,2010,39(6):69-71.[5]Wu T,Nan KH,Chen JD,et al.A new bone repair scaffold combined with chitosan/hydroxyapatite and sustained releasing icariin.Chin Sci Bull.2009;54(17): 2953-2961.[6]吴涛,南开辉,金丹,等.仿生组装纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖骨修复材料的制备及其生物相容性[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2009,11(5): 24-28.[7]王新,刘玲蓉,张其清.纳米羟基磷灰石-壳聚糖骨组织工程支架的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(2): 120-124.[8]吴涛.仿生组装淫羊藿苷控释型骨修复材料的构建与应用基础研究[D].南方医科大学博士论文,2009.[9]吴涛,南开辉,陈景帝.可控释淫羊藿苷的仿生组装骨诱导修复材料[J].科学通报,2009,54(9):1198-1206.[10]裴国献,魏宽海,金丹.组织工程学实验技术[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2006:168.[11]Polisetti N,Chaitanya VG,Babu PP,et al.Isolation, characterization and differentiation potential of rat bone marrow stromal cells. Neurol India. 2010;58:201-208. [12]Egermann M,Heil P,Tami A,et al.Influence of defective bone marrow osteogenesis on fracture repair in an experimental model of senile osteoporosis. J Orthop Res.2010;28(6): 798-804.[13]徐俊昌,吴涛,钟招明,等.瘦素对hBMSCs成骨分化的作用及机制研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009,23(2):140-144.[14]黄谦,吴涛,金丹,等.不同比例激活富血小板血浆对其生长因子浓度及人骨髓基质干细胞增殖的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008, 10(10): 965-969.[15]校月红,卢婷利,陈涛,等.药物溶血性评价方法的研究进展[J].中国药业,2012,21(17):1-3.[16]邹文,袁暾,蔡永福,等.家兔法与内毒素法检查生物材料热原的适用性研究[J].生物医学工程研究,2011,30(3):155-158.[17]Ruksudjarit A,Pengpat K,Rujijanagul G,et al.Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite from natural bovine bone . Curr Appl Phys.2008;8(3-4): 270-272.[18]王春,扶雄,杨连生. 一种新的蛋白释放载体——水溶性壳聚糖纳米粒子[J].科学通报,2007,52(1): 35-40.[19]Hu Q,Li B,Wang M,et al. Preparation and characterization of biodegradable chitosan/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite rods via in situ hybridization: a potential material as internal fixation of bone fracture. Biomaterials.2004; 25(5):779-785.[20]Liu C,Han Z,Czemuszka JT.Gradient collagen/nanohydroxyapatite composite scaffold: development and characterization. Acta Biomater.2009; 5: 661-669.[21]Cui W,Hu QL,Wu J,et al.Preparation and characterization of magnetite/hydroxyapatite/chitosan nanocomposite by in situ compositing method.J Appl PolymSci.2008;109 (4): 2081- 2088. [22]李保强,胡巧玲,汪茫,等.原位复合法制备层状结构的壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石纳米材料[J].高等学校化学学报,2004,25(10): 1949-1952.[23]Feldman GJ,Billings PC,Patel RV,et al.Over-expression of BMP4 and BMP5 in a child with axial skeletal malformations and heterotopic ossification: A new syndrome. Am J Med Genet A.2007; 143(7): 699-706.[24][Kao S,Mo J,Baird A,et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor in an animal model of spontaneous mammary tumor progression. Oncol Rep.2012;27(6): 1807.[25]Lorente-Trigos A,Varnat F,Melotti A,et al.BMP signaling promotes the growth of primary human colon carcinomas in vivo.J Mol Cell Biol.2010;2(6): 318-332.[26]赖洪华,盛朝辉,吴定奇,等.三七跌打止痛胶囊促进骨折愈合的临床研究[J]. 广西中医学院学报,2008,11(3):26-28.[27]庞健.三七片治疗骨质疏松性骨折的临床观察[J].医学信息, 2010, 23(4):142-143.[28]李学东,刘钊勇,常波,等. 三七总皂甙治疗胫腓骨骨折的临床观察[J].中国民族民间医药杂志,2011,20(3):111-111.[29]吴丽萍,陶天遵,石义刚,等.三七总甙对成骨细胞增殖、分化及OPG表达影响的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2004,10(2): 239-242.[30]张磊,李智尧,孙晋,等.三七总皂苷促进腱骨愈合的实验研究[J].中国骨伤,2011,24(2): 132-136.[31]Li X,Wang J,Chang B,et al.Panax notoginseng saponins promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells. J Ethnopharmacol.2011;134(2): 268-274.[32]王大伟,潘 华,李红波,等.三七总皂苷对酒精诱导骨髓基质干细胞分化影响的实验研究[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(8):1410-1413. |

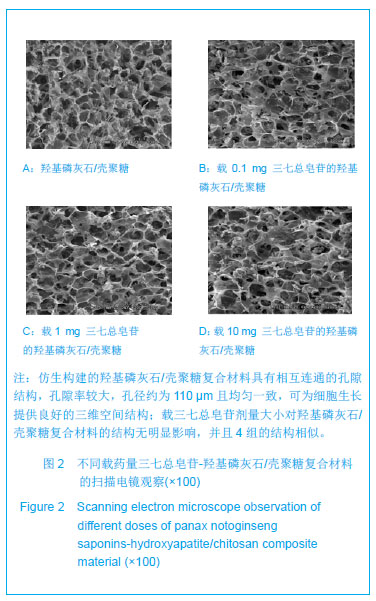

.jpg)
.jpg)